Nova:Indochina: Difference between revisions
>DLRSFluxify mNo edit summary |
>DLRSFluxify mNo edit summary |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 18:11, 12 May 2020
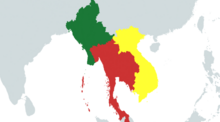
The Indochinese Peninsula (or Mainland Southeast Asia) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Siam, Vietnam, State Of Vietnam and Kampuchea.Template:Infobox locationTemplate:Infobox Region
Geography
The Indochinese Peninsula projects southward from the Asian continent proper. It contains several mountain ranges extending from the Tibetan Plateau in the north, interspersed with lowlands largely drained by three major river systems running in a north–south direction: the Irrawaddy (serving Myanmar), the Chao Phraya (in Siam), and the Mekong (flowing through Northeastern Siam, Vietnamese Laos, Vietnamese Cambodia and Vietnam). To the south it forms the Malay Peninsula, on which are located Southern Siam and Independent Malay towns; the latter is variably considered part of Mainland Southeast Asia or separately as part of Maritime Southeast Asia.
Culture
The Indochinese Peninsula is predominantly Buddhist.
Borders
The borders of Indochina have been discussed by leaders of each nation in the region (Shu, Siam, and Vietnam). The Cambodian region has been split by Siam and Vietnam. Majority of Laos is owned by Vietnam whilst some regions of Western Laos are owned by Siam. Siam owns South-East Myanmar including the city of Yangoon.